What Is Document Automation? A Complete Technical Guide
Document automation streamlines the creation of contracts, forms, and other repeatable documents by using templates, data sources, and rules to deliver fast, accurate, and scalable workflows.

Snehasish Konger
Founder & CEO
Document automation has become a foundational capability for modern businesses. I’ve seen teams waste hours rewriting the same contracts, manually pulling data from spreadsheets, and copying customer details from CRMs into PDFs. Once you automate these repetitive steps, the differences show up almost immediately: faster cycles, fewer errors, and predictable output.
This guide explains document automation in a practical, developer-friendly way. I cover how the process works, the documents you can automate, common usage scenarios, essential features to look for, and how to choose the right platform.
What is Document Automation?
Document automation refers to the process of generating documents automatically using predefined templates and structured inputs. Instead of rewriting the same legal agreement or compliance form every time, you feed data into a system that produces the final document instantly.
Most modern tools do this by merging:
Templates (Word, PDF, HTML, JSON-driven layouts)
Data sources (CRM, databases, APIs, spreadsheets)
Business rules (logic that decides what content appears in the document)
The result is a consistent, error-free document produced on demand.
How Does Document Automation Work?
Document automation follows a predictable technical workflow:
Create a template with variables (placeholders) like {{customer_name}} or {{invoice_total}}.
Connect a data source such as an API, spreadsheet, database, form submission, or CRM object.
Map the data so that each variable links to a specific data field.
Apply conditional logic that changes text, sections, or pages based on business rules.
Generate the document in your chosen format (PDF, DOCX, HTML, JSON, etc.).
Distribute or store the document with automated workflows (email, cloud storage, API callback).
A simple workflow example
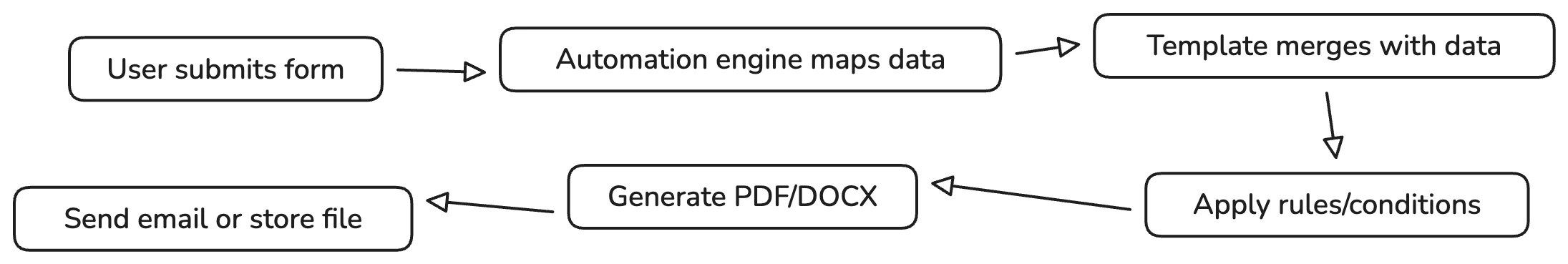
This workflow scales for everything from invoices to complex multi‑step legal and compliance documentation.
Documents That Can Be Automated
Any document that follows a repeatable structure can be automated. Some examples include:
Contracts (NDA, MSA, SOW)
Legal letters
Invoices and receipts
Quotes and proposals
HR forms (offer letters, onboarding docs)
Financial statements
Certificates
Regulatory filings
Insurance documents
Patient intake forms
Purchase orders
Reports and dashboards
If a document contains predictable sections or reusable content blocks, automation fits.
Scenarios Where Document Automation Makes Sense
You should consider document automation if you face situations like:
High document volume requiring manual effort
Frequent data entry from multiple sources
Documents requiring strict consistency and accuracy
Legal or compliance requirements
Customer onboarding with repeated paperwork
Quote and invoice generation with variable data
Multi-step workflows requiring review and approval
Many teams adopt automation after seeing error patterns—misspelled names, outdated clauses, or wrong pricing.
Benefits of Document Automation
Teams adopt automation because it reduces operational strain and improves accuracy.
1. Faster document creation
What earlier took 30 minutes now finishes in seconds.
2. Fewer human errors
Data inputs come from verified sources instead of manual copy-paste.
3. Standardized output
Your organization follows consistent structure, branding, and legal phrasing.
4. Better compliance and auditability
Automated logs provide traceability.
5. Cost reduction
Less manual effort means fewer operational overheads.
6. Integration with existing systems
Modern tools connect to CRMs, ERPs, HRMS tools, and custom APIs.
Document Automation Use Cases
Some practical use cases across industries:
Finance & Banking
Automated KYC forms
Pre-approved loan letters
Monthly statements
Healthcare
Patient intake documents
Insurance claim forms
Clinical reports
Legal
Contract generation
Lease agreements
Litigation documents
HR
Offer letters
Appointment letters
Policy document distribution
Real Estate
Property agreements
Rent receipts
Disclosure documents
Ecommerce & SaaS
Order confirmations
Renewal notices
Subscription invoices
What Are Document Automation Tools?
Document automation tools help you build templates, connect data sources, configure logic, and generate documents programmatically or on demand.
These tools usually support:
Template builders
API-based document creation
PDF/DOCX/HTML output
Conditional logic
Integrations (Zapier, Make, n8n, CRM connectors)
Some tools focus on no-code usage, while others offer advanced scripting or API automation.
Key Features of Document Automation Software
While comparing tools, you should evaluate these capabilities:
1. Template Building Options
DOCX templates
PDF templates
HTML templates
Drag-and-drop editors
2. Data Integrations
Look for direct integrations with CRMs, spreadsheets, databases, or APIs.
3. Conditional Logic
Must support:
If/else clauses
Dynamic sections
Variable blocks
Multi-step branching
4. Multi-format Export
PDF, DOCX, HTML, JSON, and email-ready outputs.
5. Workflow Automation
Tools should allow automation via:
Webhooks
Scheduling
Integrations
Approval flows
6. API Support
Developers prefer platforms with stable REST APIs for high-volume automation.
7. Security & Permissions
Important features include:
Access control
Audit logs
Encryption
How Do You Choose the Right Document Automation Software?
Choosing the right tool depends on your goals and current systems. Ask yourself:
What document formats do we need? PDF, Word, HTML?
Do we need no-code or developer-first workflows?
What integrations matter most? CRM, HRMS, ERP, API?
How complex is our business logic? Simple fills or dynamic sections?
What security requirements apply? Compliance, retention, logging.
Do we need the tool to scale? Volume matters for pricing.
Create a scoring matrix and evaluate tools across templates, automation features, integrations, scalability, pricing, and support.
Embrace Document Automation for Scalable, Error-Free Workflows
Automating documents gives your team more time and fewer errors. You remove repetitive tasks, improve operational consistency, and reduce compliance risks. Whether you’re building a contract generator, an automated invoice system, or large-scale enterprise documentation pipelines, document automation delivers measurable upside.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is document automation only for large companies?
No. Small teams use it to eliminate manual work and scale operations.
2. Can automated documents still be edited manually?
Yes. Many systems generate editable Word files or allow overrides.
3. Does document automation require coding?
It depends on the tool. No-code platforms exist. Developer-first options provide APIs.
4. Is it safe to use document automation tools for legal documents?
Yes, as long as the platform supports encryption, access control, and compliance features.
5. What data sources can feed into automated documents?
APIs, CRMs, databases, spreadsheets, and form submissions are common.
If you want, I can extend this by adding industry-specific workflows, template examples, or implementation checklists.
Share on social media





